If you have wrist tendonitis, you know how painful and debilitating it can be. Fortunately, massaging your wrists can help unlock relief from this condition. In this article, we’ll walk you through the basics of how to massage wrist tendonitis, provide simple techniques for self-massage, and discuss the benefits of massage therapy for tendonitis. With a little bit of knowledge and a few simple techniques, you can start to experience the relief you need from wrist tendonitis.
Contents
What is Wrist Tendonitis?
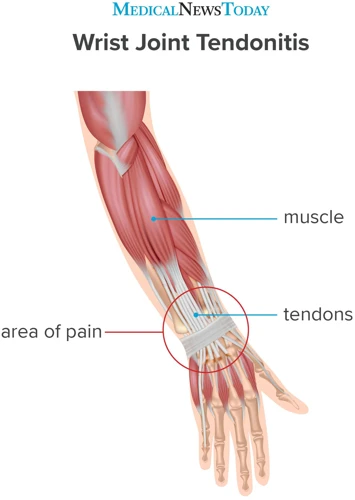
Wrist tendonitis is an inflammatory condition that causes pain and swelling in the wrist and forearm. It is caused by repetitive movements and overuse of the tendons in the wrist and forearm. The condition can become chronic if not treated properly. Symptoms may include pain, tenderness, stiffness, and difficulty using the wrist and hand.
How to Massage Tendonitis: Massaging the area can help reduce the pain and swelling associated with wrist tendonitis. Light massage with a soft brush or cloth can help to increase circulation and reduce swelling. Massage can also help loosen up tight muscles and reduce inflammation. Applying gentle pressure to the affected area with circular motions can help to relieve pain and stiffness. It is also important to avoid aggravating any existing muscle tension or inflammation.
Symptoms of Wrist Tendonitis

- Pain: Pain is usually felt at the base of the thumb, but can also spread to the forearm and elbow.
- Swelling: Swelling at the base of the thumb is often the first symptom to appear.
- Tenderness: Affected area is often tender to the touch and may even feel warm.
- Stiffness: Joints may become stiff and movement may become difficult due to inflammation.
- Weakness: Pain and inflammation may cause weakness in the affected area.
The symptoms of wrist tendonitis can range from mild to severe and can worsen over time if left untreated. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any of the above symptoms, as they can be indicators of a more serious issue.
Fortunately, massage therapy can help alleviate the symptoms of wrist tendonitis. Massage can help reduce inflammation, increase range of motion, and reduce pain. Massaging the affected area can also help loosen tightness, allowing for greater freedom of movement and increased flexibility.
Causes and Risk Factors of Wrist Tendonitis
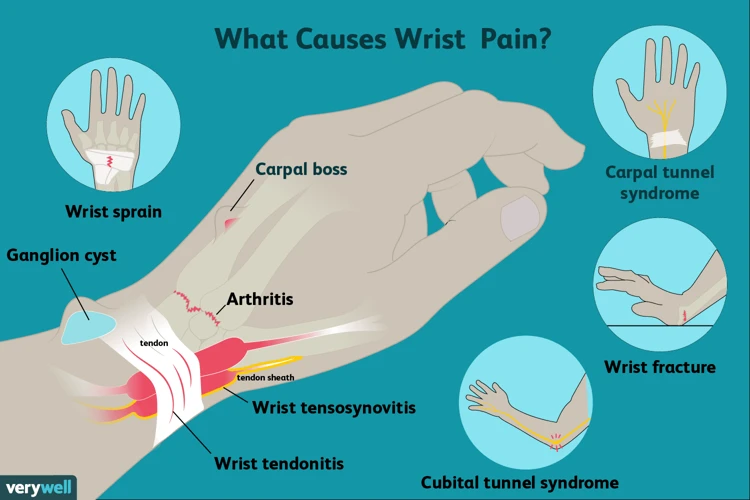
Repeated and forceful movements of the wrist can cause inflammation of the tendons and lead to wrist tendonitis. This condition is more likely to occur in individuals who are involved in activities that require repetitive movements of the wrist. Examples include playing sports such as tennis, golf, and baseball; typing on a computer keyboard; and performing manual labor.
Other potential causes and risk factors of wrist tendonitis include:
- Injury to the wrist
- Bone spurs
- Arthritis
- Tight muscles or lack of flexibility in the wrist and forearm
- Poor posture
- Improper technique or form when performing repetitive wrist movements
Individuals who are over the age of 40 are more likely to develop wrist tendonitis due to age-related wear and tear of the tendons.
How to Massage Wrist Tendonitis
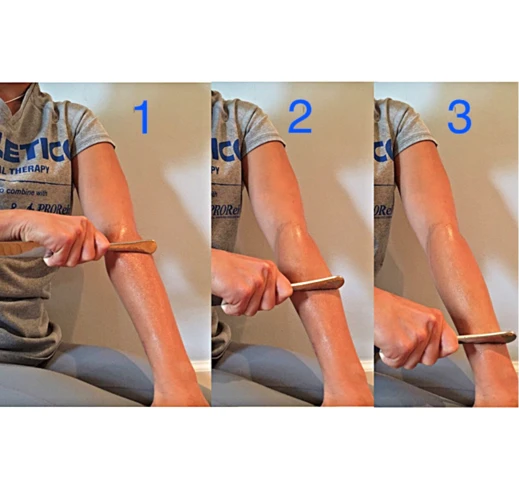
Preparation
Heat therapy: Applying heat to the wrist can help to reduce inflammation and relax the muscles. Use a heating pad or warm compress for 10 to 15 minutes at a time.
Massage Techniques
Friction massage: Massage the tendon, with firm pressure, in a circular motion for 10 to 15 seconds.
Trigger point massage: Apply deep pressure to the trigger points for 10 to 15 seconds.
Cross friction massage: Place your fingers on the tendon and move them in a circular motion, for 10 to 15 seconds.
Petrissage massage: With your thumb, massage the tendon in a circular motion, for 10 to 15 seconds.
Friction Massage

Friction massage is one of the most effective techniques for relieving wrist tendonitis. This massage technique involves rubbing the affected area in a circular motion with deep pressure. It can help to break down any adhesions in the muscles and tendons, as well as increase circulation and reduce inflammation. To perform a friction massage, start by applying firm pressure to the affected area and rubbing in circular motions. Increase the pressure gradually, and continue to apply consistent pressure for about one minute. The friction massage should be repeated two to three times a day for best results.
Trigger Point Massage
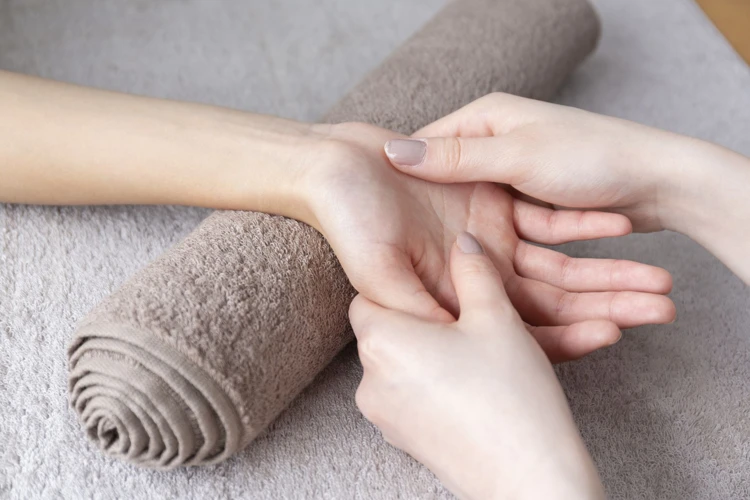

- Trigger Point Massage is a method of applying concentrated pressure to particular points on the body. These points are known as trigger points, and are believed to be areas of increased sensitivity or muscle tension.
- Trigger Point Massage is an effective treatment for relieving pain and tension in the muscles and soft tissues. It can help reduce inflammation and improve range of motion.
- Trigger Point Massage is often used to treat conditions such as neck and shoulder pain, back pain, chronic headaches, and fibromyalgia.
- It is believed that applying pressure to these trigger points can help to reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and decrease pain.
- Trigger Point Massage can be done with the hands, elbows, or other tools such as rollers and balls.
- It is important to consult a qualified massage therapist to ensure that the massage is done correctly and to avoid injury.
Cupping
- Place your cupping tool (such as a small cup) on the affected area.
- Gently move the cup in a circular motion for 30 seconds.
- Apply more pressure to the affected area for 30 seconds.
- Move the cup again in a circular motion for 30 seconds.
- Remove the cup and massage the area with your fingers for 1 minute.
Cupping is a form of massage therapy that uses suction to improve circulation and reduce inflammation. It is a great technique to help relieve pain and stiffness in the wrist caused by tendonitis. Cupping can also help to reduce swelling and promote healing of the affected area.
Benefits of Massage for Wrist Tendonitis

Massage is an effective way to treat wrist tendonitis and can help reduce pain and discomfort. It can also help improve flexibility and range of motion, as well as reduce inflammation. Massage can be used to target specific areas of the wrist and forearm, which can allow for more targeted treatment of the problem area. Massage can also help improve circulation, which can help reduce swelling and inflammation.
Table of Benefits of Massage for Wrist Tendonitis
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduce Pain and Discomfort | Massage can help reduce pain and discomfort from wrist tendonitis. |
| Increase Flexibility and Range of Motion | Massage can help improve flexibility and range of motion in the wrist and forearm. |
| Reduce Inflammation | Massage can help reduce inflammation, which can help reduce swelling and discomfort. |
| Target Specific Areas | Massage can be used to target specific areas of the wrist and forearm, allowing for more targeted treatment. |
| Improve Circulation | Massage can help improve circulation, which can help reduce swelling and inflammation. |
Massage can be a great way to treat wrist tendonitis and can provide many benefits, including reducing pain and discomfort, increasing flexibility and range of motion, reducing inflammation, targeting specific areas, and improving circulation. By utilizing these techniques, you can help unlock relief from your wrist tendonitis.
When to See a Doctor for Wrist Tendonitis

Tendonitis of the wrist can be a very painful and debilitating condition. If not treated properly, it can worsen over time and cause more significant damage. If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice:
- Severe pain in the wrist
- Swelling of the wrist
- Redness of the wrist
- Difficulty moving the wrist
- Shooting or throbbing pain
- Numbness or tingling in the wrist
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice and get a diagnosis. Your doctor may recommend rest, medication, physical therapy, or even surgery depending on the severity of your condition. In some cases, massage therapy can be beneficial in treating wrist tendonitis, but it’s important to consult your doctor before trying any massage techniques to ensure you are not causing further harm.
Complications of Wrist Tendonitis
Wrist tendonitis can develop into a chronic condition if left untreated. Symptoms may include persistent pain and tenderness in the wrist, difficulty moving the wrist, decreased grip strength, and swelling around the affected area. If complications occur, they can include:
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Carpal tunnel syndrome | Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by swelling around the median nerve as it passes through the wrist. Symptoms may include pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness. |
| De Quervain’s disease | De Quervain’s disease is a condition that affects the tendons in the thumb. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the thumb. |
| Trigger finger | Trigger finger is a condition in which the finger is stuck in a bent position and cannot be straightened. Symptoms may include pain, stiffness, and a clicking or popping sound when the finger is moved. |
If you are experiencing any of these complications as a result of wrist tendonitis, it is important to seek medical attention. Massage therapy can help to reduce pain and improve mobility, but it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions for treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Types of Massage Techniques are Best for Relieving Wrist Tendonitis?
Trigger Point Massage – This type of massage involves applying pressure to specific tense areas of muscle tissue to reduce pain and tension. This can be done manually or with the use of a tool such as a massage ball.
Myofascial Release – This massage technique is a gentle, sustained pressure on the fascia, the connective tissue surrounding the muscles. It helps to release tension and improve flexibility in the wrist.
Friction Massage – This type of massage uses a circular motion to massage deep into the muscles. It is used to break up scar tissue and adhesions that form in the wrist from overuse.
Sports Massage – Sports massage techniques are designed to improve performance and reduce the risk of injury. These techniques include compression, joint mobilization, and stretching.
Swedish Massage – This type of massage uses long, sweeping strokes to relax the body. It helps to reduce stress and improve circulation, which can help to reduce inflammation and improve mobility in the wrist.
Acupressure – This massage technique involves applying pressure to specific points on the body to relieve pain and tension. It can be used to treat wrist tendonitis by stimulating the muscles and tendons in the wrist.
What are the Benefits of Massaging the Wrist for Tendonitis?
- Reduce Pain: Massaging the wrist can help reduce pain in the affected area. It helps to alleviate tension and relax the muscles in the wrist, which can help reduce pain.
- Increase Mobility: Massaging the wrist can help improve mobility and flexibility of the joint. It helps to loosen the muscles and tendons, allowing for better range of motion.
- Reduce Swelling: Massaging the wrist can help reduce swelling, which can help reduce pain and improve mobility.
- Improve Circulation: Massaging the wrist can help improve circulation, which can help reduce inflammation and speed up healing.
- Reduce Stress: Massaging the wrist can help reduce stress, which can help reduce tension and help improve overall wellbeing.
How Often Should I Massage My Wrist For Tendonitis?
Frequency of massage depends on the severity of the tendonitis and the individual’s physical capacity to handle massage. Generally, it is recommended to massage the affected area twice a day – once in the morning and once in the evening. A massage session should last for 5-10 minutes and should include gentle, soothing strokes. Do not press too hard and stop if any pain or discomfort is felt. If massage is too painful, reduce the intensity or frequency of massage.
What Should I Do If I Experience Pain While Massaging My Wrist?
If you experience pain while massaging your wrist, stop immediately and apply ice to the affected area. Once the pain has subsided, reduce the pressure you are applying and slowly increase it again. If the pain persists, it is best to consult your doctor.
What other treatments may be helpful for wrist tendonitis in addition to massage?
- Exercises: Gentle stretches and strength-building exercises can help reduce inflammation and improve range of motion.
- Rest: Taking breaks from activities that aggravate wrist tendonitis can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Splints: Wearing a splint at night can help keep the wrist in a neutral position while sleeping to reduce pain.
- Medication: Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen can help reduce swelling and pain.
- Injections: Steroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and pain.
Conclusion
Massage therapy for wrist tendonitis can help to reduce inflammation and pain, improve range of motion and flexibility, and promote healing. Applying these simple techniques can make a world of difference in relieving the pain and discomfort associated with wrist tendonitis. It is important to talk to your doctor before beginning any type of massage therapy to ensure it is safe and suitable for your individual needs.